Welcome back to Open Pioneers #32.
It’s been a few months since my last newsletter. Life and my job at the Linux Foundation kept me busy, but I have set myself the goal of writing weekly again from now on.
I’m also using this relaunch to change a few things: Besides the fresh branding, I switched my newsletter platform from Beehiiv to Substack. I also decided to make the content more personal and do more deep dives into open source topics that I’m interested in. I will still be featuring open source alternatives, announcing funding rounds or interesting jobs in the open source sector, but more as a side note.
I've cleaned up the subscriber list and only left people on it who have opened my emails regularly, as I don't want to spam anyone.
That said, I'm very excited to kick this off again. There is so much exciting stuff happening in open source, and I'm looking forward to keep learning about it with you!
The State of Open Source LLMs
Open source large language models (LLMs) have evolved from niche academic projects into robust, community-driven platforms that challenge proprietary giants like Microsoft or Google. Today, open source LLMs not only promote transparency and collaboration, but they also enable a more cost-effective and adaptable approach to AI development.
A New Era of Commoditized AI
The open source movement in AI has grown exponentially over the past few years. Instead of relying solely on expensive, closed models from major tech companies, developers and researchers worldwide can now access, modify, and improve upon state-of-the-art LLMs. This commoditization is critical for ensuring that AI is accessible to everyone, from indie hackers over startups to academic institutions.
Recent developments have shown the potential of open source LLMs. For example, Chinese DeepSeek’s R1 model has gained world-wide attention for matching the performance of leading models like OpenAI’s o1 - while being trained at a fraction of the cost and computational power. DeepSeek’s use of reinforcement learning and a mixture-of-experts architecture enables it to activate only a subset of its 671 billion parameters per query, thereby reducing energy consumption and hardware requirements.
Benefits and Challenges for Open Source LLMs
Open source LLMs offer several compelling benefits:
Transparency and Trust: With publicly available training data, source code, and model weights, open source LLMs allow for thorough scrutiny, making them less of a “black box” compared to proprietary counterparts. This transparency leads to community trust and collaborative troubleshooting.
Low Costs: Open source models lower the barrier to entry. The cost efficiency of open source is particularly beneficial for academic institutions and start-ups with limited resources - in other words: it promotes innovation.
Customization and Flexibility: Open access means that developers can fine-tune models for niche applications, integrating domain-specific knowledge or even adapting models for local languages—a key consideration for initiatives like OpenEuroLLM, which seeks to serve Europe’s linguistic diversity.
However, challenges remain. Open source LLMs can be vulnerable to adversarial attacks, and the quality of available training data may vary. Moreover, while open models promote innovation, they also raise questions about responsible usage, as powerful AI tools in the wrong hands could lead to misuse. Balancing openness with safety is an ongoing conversation within the community that we need to take seriously.
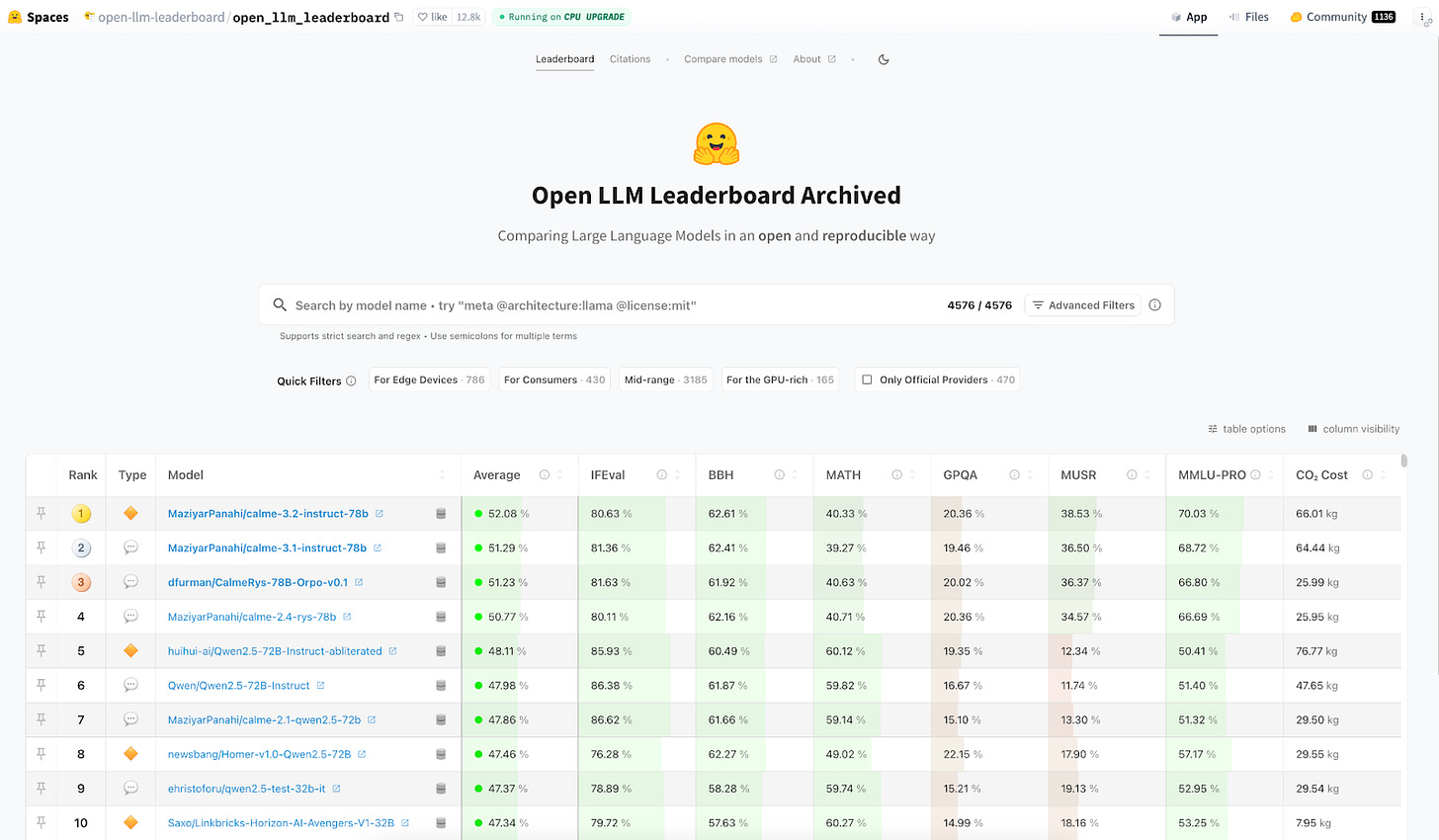
Key Open Source LLMs You Should Know About
Below is a snapshot of the current open source landscape according to the Hugging Face Open LLM Leaderboard.
The following open source LLMs stand out to me, because they get mixed and matched a lot by the broader AI community:
Llama 3.1 (Meta): The Meta’s Llama 3.1 series - from smaller models up to a massive 405B-parameter version - consistently ranks high on general text generation, multilingual processing, and coding tasks.
Mistral Large 2 (Mistral AI): With a powerful 123B-parameter architecture and an impressive context window (up to 128K tokens), Mistral Large 2 excels in both language understanding and coding tasks. Its sparse mixture-of-experts design optimizes performance while reducing inference costs, making it a leader in efficiency and scalability.
DeepSeek R1 (DeepSeek): DeepSeek’s R1 model leverages reinforcement learning and a mixture-of-experts approach to deliver competitive reasoning, mathematics, and coding capabilities. Although DeepSeek allegedly uses less sophisticated hardware compared to its Western competitors (there is a US export ban on China for Nvidia GPUs), it achieves high performance at a fraction of the training cost. A fact that has led to lots of discussions - even in mainstream media.
DeepSeek v3 (DeepSeek): Building on the R1 series, DeepSeek v3 leverages a 671B-parameter Mixture-of-Experts architecture—with 37B activated parameters per token—to deliver impressive efficiency in general text generation, multilingual processing, and coding tasks.
Qwen 2.5 (Alibaba): Alibaba’s Qwen 2.5 has made waves with its strong multilingual capabilities, specialized performance in coding and mathematical reasoning, and efficient deployment strategies. Its open-source components are released under the Apache 2.0 license.
Falcon-180B (Technology Innovation Institute): The Falcon-180B model is a testament to the capabilities of large-scale open source LLMs. Trained on over 3.5 trillion tokens, it provides top-tier performance on a variety of benchmarks, making it one of the most competitive open source alternatives available.
An Outlook
As investments in open source AI continue to rise, industry players like Meta and community initiatives across Europe and beyond are doubling down on the potential of collaborative AI development. With companies releasing their models under permissive licenses and sharing extensive technical details and benchmarks, the LLM ecosystem is set for rapid disruption.
Most experts believe that the future of AI will be built on the foundation of open source, where shared knowledge accelerates innovation and leads to more equitable technological advances.
I think this future has just begun.
New & Hot Open Source Projects 🔥
Second Me: An open source prototype where you craft your own “AI self”: a new AI species that preserves you, delivers your context, and defends your interests. GitHub
Cursor Talk to Figma MCP: A Model Context Protocol (MCP) allowing Cursor to communicate with Figma for reading designs and modifying them programmatically. GitHub
Classless.css: A lightweight CSS framework for websites with impeccable taste but zero desire to add classes. GitHub
Open Source Funding Rounds 💸
Supabase, an open source Google Firebase alternative, raised $100M at a $2B valuation. Link
AheadComputing, a player from the RISC-V ecosystem, announced their $21.5M Seed. Link
Rerun, creators of a framework for logging and visualizing multimodal data, raised a $17M Seed led by PointNine. Link
Onyx, an open source enterprise search solution, raised a $10M Seed co-led by Khosla Ventures and First Round Capital. Link
Lingo.dev, creators of an open source localization toolkit, raised $4.2M. Link
Until next week,
Jonathan (@jonathimer)